PRTG Network Monitor, by Paessler, takes a sensor-based approach to monitoring. A PRTG sensor is a basic monitoring element, which might monitor, for example, the space available on a disk drive or the CPU load of a server. The benefit of this model is PRTG can function as a free uptime monitoring tool, provided you use fewer than 100 sensors. WebWatcher for Mac begins monitoring and recording all historical activity discreetly and then sends it to your secure online account. Work Examiner’s monitoring tools show every type of computer activity performed by your employees in real-time: web surfing, keystrokes, messaging, printing, or downloading. Diligent monitoring supports disabling any unwanted feature. Additionally, switching between Stealth and Tray Icon modes allows the software to run with. Most network monitoring software on Mac monitor both network and hardware activity on your Mac although you’ll usually find that some apps are more focuses on one than the other. The good news is that some of the best network monitoring for software for Mac is either free or costs very little. MacOS even has its own free network monitoring.
Uptime is of critical importance for your company’s networks and systems, alongside its website and web service delivery. It has a direct impact on your company’s ability to support end users and deliver services. Not maintaining high levels of uptime can significantly interfere with a business’s ability to work productively or impact user satisfaction by making a website inaccessible. Either way, it can translate into significant financial losses.
However, establishing high uptime for any element of your network or infrastructure can be tricky. There are numerous components potentially contributing to downtime, and these triggers need to be monitored to reduce the risk of downtime occurring on your systems. Because there are so many potential downtime triggers, manual monitoring is a difficult, time-consuming, and resource-consuming task. Employing an uptime monitor is a highly effective way of maximizing availability in the most economical way possible.
There are many server uptime monitoring tools for you to choose from, including open-source, closed-source, enterprise-grade, and free uptime monitoring programs, each with its own merits and disadvantages. In this guide, I’ll help you decide between the best uptime monitoring software, open source and closed source, on the market. I’ll also give consideration to the best free server uptime monitoring software, for those of you who have your heart set on an unpaid solution.
Before going into the best network uptime monitors, I’ll first outline the basics of uptime monitoring. For those who don’t have time to read the full guide, a quick summary: I consider SolarWinds® ipMonitor® to be the best server uptime monitoring tool available. It offers an impressive range of functionalities, all of which are sophisticated and useful, while delivering a user-friendly and accessible dashboard and interface. If you want uptime alerts and diagnostics embedded in a more complete network solution, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor provides extensive monitoring tools for on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
Skip to “The Best Uptime Monitors” List >>>

With regard to free server uptime monitoring tools, a free edition of ipMonitor is available and is well-regarded among experienced administrators. SolarWinds itself has a reputation for producing some of the best monitoring and management tools across the board.
What Is Uptime?
Uptime is a measure of the percentage of time an element of your network or system is working as intended. Website uptime specifically refers to the time a web service or website is live and available to users over a given period. For any element of your system, whether it’s the network, hardware, system, or website, the aim is to establish close to 100% uptime, meaning the system element is constantly available. Industry standards consider 99.999% uptime to be indicative of high availability. This is because every element of your system experiences downtime at one point or another, planned or not. By considering 99.999% uptime, otherwise known as “five-nines availability,” as high availability, the industry acknowledges the reality of occasional downtime while still aiming for near-constant uptime.
How to Calculate Uptime Percentage
In its most basic form, uptime is the downtime subtracted from the total time. The formula for calculating the percentage of uptime, as stated above, is simply uptime divided by total time. An uptime of 99.999%—high availability—allows for 5.25 minutes of downtime in a single year.
Five-nines availability, however, is difficult to achieve. If the system or service is mission critical, as with hospital systems, then five-nines availability should always be the goal, because any downtime could have dire consequences. However, for systems and services not considered mission critical, 99.99%—which translates to 52 minutes and 36 seconds of downtime each year—is considered a good uptime ratio. A ratio of 99.98%—70 minutes and 7 seconds of downtime each year—is thought of as decent, and for some businesses might not pose a financial liability.
Bear in mind, these figures account for actual availability, but don’t represent other factors, like function and overall performance. A system or service can experience other issues making them potentially unusable, even if high availability is achieved.
Cost of Downtime
According to a 2016 study by Exigent, an hour of down time, depending on the size of the business, can cost an organization between $9,000-$700,000 with an average of around $164,000 of lost revenue per hour. This figure is supported by a study conducted by Information Technology Intelligence Consulting in 2019, in which 98% of businesses surveyed claim one hour of downtime costs them at least $100,000. Also, about one-third of businesses in the study claim a single hour of downtime can cost $1 million, and sometimes more than $5 million.
Downtime costs are determined by several factors, including how many employees would be impacted if critical data became unavailable, the average hourly wage of the impacted employee, the per-hour overhead cost of the impacted employees, and the amount of revenue lost per hour because of data unavailability.
Main Causes of Downtime
Understanding the multiple and common factors causing downtime can help you prevent it from happening—and assist you in fixing it when it does. It also emphasizes the importance of having an effective up/down monitoring strategy or server uptime tool designed to cope with the full range of downtime triggers.
In the Exigent study, network outages were found to be the most common reason for downtime, accounting for about half. The study also found while network outages account for 50% of down time, human error is the leading cause of downtime by data volume and among large volume sites. Human error accounts for 58% in large volume sites and 44% in others. Overall, human error accounts for 45% of all downtime. Other common causes of downtime of note in the report include:
- Server failures
- Storage failures
- Application errors
- Power outages
- Usage spike and/or surges
Best Uptime Monitors
Given the cost of downtime and the range of factors potentially causing or contributing to it, having an effective uptime monitor at your disposal is fundamental to a successful business continuity plan. The following products have been chosen with consideration of their user-friendliness, their range of capabilities, how advanced they are, and their suitability for business use.
SolarWinds ipMonitor is a lightweight network uptime monitor designed to provide monitoring for up to 2,500 servers, network devices, and applications. It affords you visibility into device, CPU, disk usage, and memory status, and flags performance issues associated with key processes and services.
Like all SolarWinds products, ipMonitor benefits from a dashboard designed in an intuitive way to make navigation quick and easy. In the main toolbar, which is located at the top of the web console, you’ll have access to all the resources, settings, and options associated with the application. Because all components are sensibly and centrally located, there’s practically no navigational learning curve.
There are five main web console elements: Dashboard, Devices, Reports, Configuration, and Resources. The Dashboard tab displays event data, while the Devices tab shows the status of selected monitors and devices. Reports are configurable and provide monitoring data on network devices. The Configuration tab gives you access to all configuration settings, and Resources lets you access THWACK®, the SolarWinds online help and support community.
SolarWinds ipMonitor includes multiple monitor types, which observe your system applications, servers, infrastructure equipment, and resources on a round-the-clock basis. Once a device monitor has been configured, it’ll show the device’s status within the dashboard. There’s a broad range of monitors available, including an Active Directory monitor, a bandwidth monitor, a battery monitor, a drive space monitor, a file directory monitor, an event log monitor, a finger monitor, an FTP monitor, a gopher monitor, and a PING monitor.
ipMonitor is incredibly user-friendly, despite offering some considerably advanced features. As an example, accessing monitor types and adding new monitors is a simple three-step process. Just visit the Devices tab, locate and click the device you want to monitor, then select “Add New Monitor” from the drop-down menu.
The alerts system is also noteworthy. The software functions by using background processes (monitors) to confirm device resources are operating correctly. When a resource reaches a critical range (e.g., CPU utilization of 95%), this information is displayed in the dashboard. To make sure you never miss key information, you can set up alerts, and the program will notify you via text, email, or an alternative supported notification whenever a problem is found.
The alerts system is versatile, allowing you to configure individual alerts to be responsible for a single monitor, multiple monitors, or groups of monitors. You can create unlimited actions within each alert, schedule each action to be executed independently, and specify how the problem is to be escalated if necessary. The escalation setup is easy: you simply define how many monitor failures are allowed to occur before a certain action is triggered and establish when alerts are to be shared with certain parties.
You can get ipMonitor up and running within minutes, which is another notable advantage of this program. Because it runs on one machine with low system requirements and utilizes flat file storage, it has a lightweight footprint, and there’s no separate database to be maintained. This server uptime tool is cost-effective, with a monitor-based pricing model to ensure you only pay for what you need. A free 14-day trial of ipMonitor is available.
This is a free uptime monitoring solution providing a quick and agentless approach to safeguarding and boosting availability. Like the paid alternative, SolarWinds ipMonitor Free Edition benefits from an easy-to-use dashboard, with five main pages located in the top navigation bar: Dashboard, Devices, Reports, Configuration, and THWACK. This program is surprisingly generous, considering you don’t have to pay a single dollar for it. It enables you to monitor applications, servers, and network devices. Assuming your needs are limited to a small environment, this uptime monitor offers an essential IT monitoring solution.
The free version of ipMonitor supports alerts, keeping you up to date on any performance or availability issues. It’s capable of automating remediation actions, and it gives you access to built-in reports to help with planning and troubleshooting. The tool provides essential status and performance insights into up to 50 monitors, including up down device status. You’ll gain visibility into CPU, memory, and disk usage, and any performance issues associated with critical processes and services.
Under the Configuration tab, you can configure alerts to help you uncover failures before they impact your users. You can name an alert whatever you like, enable it, and determine whether listed or unlisted groups, devices, and monitors are to be alerted. You can also set up actions to be triggered by each alert. Corrective actions taken by the software could include rebooting a server or executing a script.
This tool runs on one machine, with minimal system requirements, so it’s great for small environments. The startup wizard offers you tips and recommendations on configuration settings, enabling you to start monitoring within a matter of minutes. And with automatic discovery of devices, you don’t have to waste time adding each manually.
This 100% free server uptime monitoring software is ideal if you have low requirements, but it’s not especially suited to business use. You can request an email link to ipMonitor Free Edition by entering your details here.
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is an extensive network monitoring tool designed to help you ensure your critical business services are always reachable. The tool offers network uptime monitoring solutions for a wide range of vendors to help reduce downtime and optimize network infrastructure.
NPM includes fault, performance, and availability monitoring as well as hop-by-hop network path analysis to help ensure your business services are being delivered without interruption. The tool also includes cross-stack network data correlation services designed to help you get to the root cause of downtime quickly. With NPM, you can drag and drop network performance metrics onto a shared timeline, so you can see an immediate visual correlation of the data from across your network.
NPM goes even further when it comes to data correlation. The tool also lets you automatically discover and map devices from across your network, while collecting and correlating performance metrics, wireless coverage, and link utilization, so you can clearly see everything occurring on your network. This visibility means you can troubleshoot outages and other issues capable of causing network downtime before they impact your network and your users.
One of the most useful features in NPM is NetPath—a feature giving you insight into what’s happening both inside and outside your network. The NetPath feature lets you view traffic, configuration, and performance details of your network devices and applications in cloud, on-prem, or hybrid environments. With NetPath, you’re able to quickly prove your network’s mean-time-to-innocence, meaning you know when to contact external network providers regarding internet connectivity and thus uptime.
Like other SolarWinds offerings, NPM comes with high-quality, intuitive dashboards and automated intelligent alerting, capacity forecasting, and reporting designed to help you prevent network downtime. NPM offers a fully-functional free 30-day trial.
PRTG Network Monitor, by Paessler, takes a sensor-based approach to monitoring. A PRTG sensor is a basic monitoring element, which might monitor, for example, the space available on a disk drive or the CPU load of a server. The benefit of this model is PRTG can function as a free uptime monitoring tool, provided you use fewer than 100 sensors. You can choose whichever sensors you want, which means PRTG can be entirely tailored to your specific needs.
Moreover, if you want to expand on your up down monitoring solution to create a more comprehensive, one-stop monitoring tool, PRTG Network Monitor allows you to do so. It serves as an all-in-one solution if you so choose, offering jFlow monitoring, firewall monitoring, IP monitoring, IP SLA monitoring, jitter monitoring, packet sniffing, and much more. In other words, it’s what you make of it.
Another advantage of PRTG Network Monitor is it has a customizable notification system, which can alert you via text, push notification, or email when anything goes wrong. You can set alert thresholds yourself, ensuring you don’t get an unnecessary flood of alerts but will be notified of any activity you consider to be critical.
You’ll need approximately five to ten sensors for each device, or one sensor for every switch port, meaning PRTG Network Monitor can become costly quickly. Moreover, the licenses set a limit for the number of sensors you can use, and once this limit is exceeded, you’ll have to upgrade to a higher paid plan. The issue with this model is if you breach one plan’s sensor limit but don’t necessarily utilize the full sensor provision of the higher plan, you may end up paying for more than you need. For this reason, PRTG is not always cost-effective.
A 30-day free trial of PRTG Network Monitor is available. The trial version is completely unlimited and reverts to the free edition of PRTG at the end of the 30 days, so you won’t have to worry about a surprise bill.
Site24x7, a well-known name among IT administrators, has an agentless website monitoring tool available designed to allow you to monitor URLs across the intranet, internet, and 3G/4G networks. It also lets you perform synthetic web monitoring from a range of ISP networks, ensuring your website users are uninterrupted and maximum uptime is achieved.
This program is suitable for monitoring the uptime and performance of IPv4/IPv6 enabled websites from more than 90 locations across the globe. Monitoring capabilities are advanced, covering domain expiry, SSL/TLS certificates, and website defacement. You can even receive notifications directly to your mobile phone when a problem is identified.
Site24x7 gives you insight into website response time, including DNS time, time to first byte, connection time, SSL handshake time, download time, and much more. You can analyze how your website responds when it’s accessed from different global locations, and accumulate detailed data pertaining to everything from the SSL/TLS protocol version being used to cipher suite details.
The tool’s user interface is another noteworthy benefit. The layout makes data interpretation easy, as it’s both dynamic and uncluttered, with graphical representations of data in the form of line charts, scatter graphs, and geographical maps. Still, I find Site24x7 could be more user-friendly and its range of functionality expanded upon. You can sign up for a 30-day free trial here.
Server Density offers cross-platform monitoring for Windows, Linux, Docker, FreeBSD, Mac, and Kubernetes. Its powerful API conducts automatic agent installation, and the program can be integrated with over 100 systems and services. This includes MySQL, MongoDB, Varnish Cache, Redis, Elasticsearch, Apache, PostgreSQL, RabbitMQ, Couchbase, and much more.
The best thing about this program is its user interface, which makes uptime monitoring surprisingly engaging. The design highlights and draws attention to the most critical metrics, like website availability and the number of activated alerts, so they can’t be overlooked. Another benefit is Server Density is part of StackPath, a web services platform for speed, scale, and security. This means using Server Density affords you the opportunity to expand your up down monitoring solution into a wider IT monitoring and management strategy, through a single unified platform.
Though the dashboard is super dynamic and facilitates at-a-glance visibility of your systems, learning to navigate it and take full advantage of its features can take time. A 14-day free trial is available, with no credit card details required.
ManageEngine OpManager is another all-in-one monitoring solution for IT administrators. It offers real-time network monitoring with more than 2,000 built-in network performance monitors covering latency, errors and discards, speed, packet loss, and more. It also includes physical and virtual server monitoring, covering CPU, memory, and disk utilization on Linux and Windows servers, and VMware, Xen, Hyper-V, and Nutanix server virtualization platforms. In addition, it provides WAN link monitoring capabilities allowing you to view hop-by-hop performance, to facilitate rapid root cause identification.
OpManager gives users a comprehensive SNMP monitoring experience designed to use automatic network discovery to keep itself up to date. It can discover up to 15,000 interfaces per minute, which is indicative of a seriously powerful program.
OpManager employs multi-level thresholds, giving you the opportunity to narrow down and specify your alerts, which will notify you instantly if a violation occurs. I’m also a big fan of the customizable dashboards, which let you choose between and organize more than 200 performance widgets. My only real issue with OpManager is navigating it and locating the various utilities can be complicated and time-consuming. You can schedule a demo if you want to know more.
Built on the open source components of Nagios Core, Nagios XI is an uptime monitor available for Windows, VMware Workstation/vSphere/ESX, CentOS, RHEL, Ubuntu, and Debian Linux. This tool not only assists you with reducing downtime, but also detects network incidents and monitors the overall health of your whole network. Nagios XI monitors all mission-critical infrastructure components, including operating systems, applications, services, system metrics, network infrastructure, and network protocols. There are hundreds of third-party add-ons available, meaning you can monitor almost all in-house services, systems, and applications. This flexibility is the greatest advantage of Nagios XI.
Layout, design, and preferences are customizable on a per-user basis, offering team members maximum flexibility. The program also offers multi-tenant capabilities, so the web interface can be accessed by stakeholders. Views are user-specific, meaning clients only see infrastructure components for which they’re authorized.
To help you get set up, Nagios XI offers both a remote assist and a quick-start module, which can save you much time. While this assistance is appreciated, its requirement makes Nagios XI less user-friendly than some other programs. This may put some users off; however, keep in mind lots of support is available and the tool itself is sophisticated.
The free version of Nagios, Nagios Core, is a popular choice among IT administrators who prefer open source programs. The major benefits of open source tools are the lack of vendor lock-in, the lower software costs, and the abundant support available. Still, generally speaking, open source programs aren’t as suited to enterprise-level requirements as closed source programs.
Zabbix is free uptime monitoring software, open source and designed to monitor everything including network, cloud, applications, and servers. It has specific solutions for various industries, covering education, marketing, IT and telecommunications, retail, and more. With Zabbix, you’re able to view when a service is in a critical state and when it’s down. The tool’s performance monitoring capability is one of its most notable advantages—you’re able to monitor disk space, fan status, device temperature, and even power supply. This gives you insights into your device to help you prevent it from failing.
As an all-in-one solution, Zabbix is also capable of monitoring your network traffic, ensuring your connection remains fast and available to every device on your network. To keep up to date, Zabbix conducts regular network discovery scans, adding new devices when appropriate. Whenever a new device is found, a discovery event is generated. According to your settings, the program will then either send you a notification, execute a remote script, or add or remove the host.
Zabbix is among the best free monitoring tools. The issue, again, is open source programs are not as reliable, in an enterprise environment, as closed source solutions.
Getting Started with a Server Uptime Tool
Overall, SolarWinds ipMonitor beats the competition by combining ease of use and beginner-friendliness with some seriously advanced features. SolarWinds is dependable and well supported, with a community of loyal users accessible via the THWACK interface, and technical support operatives on hand 24/7. With an impressive and reliable alerts system, a wide range of monitors, and a monitor-based pricing model, ipMonitor is cost-effective and comprehensive, providing a scalable and reliable enterprise-grade solution.
Way back in 2015, we reviewed the must-have top free networking tools. And honestly, those reviews have stood the test of time. But now that time has passed, the landscape has changed, and we think it’s worthwhile to review those old choices and possibly add a few new ones.
Manage and maintain Windows®, Linux® and Mac® OS servers, workstations & laptops. Wrapped in a single, all-in-one solution, Naverisk provides tools for device and network scanning & IP monitoring, alerting, auditing, patching, reporting, ticketing, workflow, automation, scripting, and much more. Intel® Power Gadget is a software-based power usage monitoring tool enabled for Intel® Core™ processors (from 2nd Generation up to 10th Generation Intel® Core™ processors). Intel® Atom™ processors are not supported. For Mac Using the Intel® Power Gadget API on Mac OS X. For Windows Using the Intel® Power Gadget API on Windows. Network Bandwidth Analyzer Pack. I’m a big fan of this bandwidth monitoring software bundle from.
Laying the Foundation
To build a network, you start with an architecture, draw the design, and analyze and choose the hardware that meets your requirements. Because many organizations need their network to be up and functioning to generate revenue, having the right set of tools to monitor and manage the one you so lovingly created is critical.
But how do you find the best network monitoring tools when there are hundreds of commercial products, freeware tools, and open-source software to choose from? While the debate about free versus commercial goes on, there are tried and tested, free network monitoring tools that many network admins swear by. Below, we will share some of our favorites with you.
But first…
Open-source choices are good and can even match commercial tools, but you should know that using open-source monitoring requires a high level of involvement with the tool, which may not perfectly suit your needs. As the saying goes, “Open-source is only free if your time is worthless.”
Open-source monitoring solutions often require a significant investment in time and resources. Missing features may have to be built with the help of community support or an in-house IT team. The second consideration is security, which may become an issue, depending on the tool you select and your enterprise’s security guidelines. Additionally, immediate custom fixes may not be available unless you spend time developing and maintaining them yourself.
When we need a network monitoring tool that is easy to install, and supports monitoring and reporting out of the box, we like SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor (NPM). NPM acts as a single pane of glass to provide complete and comprehensive network monitoring capabilities that complement some of the essential free tools you may already use.
Knowledge Base
Because enterprise networks are becoming bigger and more complex, it’s important to put network monitoring and managing solutions in place early in the implementation phase.
What’s on the list?
If you do decide to go the free/open-source route, you should check out the following. It’s our list of the best free network monitoring tools available today.
Nagios Core
Nagios® is the great-grand-daddy of monitoring tools, with only ping being more ubiquitous in some circles.
Nagios is popular due to its active development community and external plug-in support. You can create and use external plugins in the form of executable files or Perl® and shell scripts to monitor and collect metrics from every hardware and software used in a network. There are plugins that provide an easier and better GUI, address many limitations in the Core®, and support features, such as auto discovery, extended graphing, notification escalation, and more.
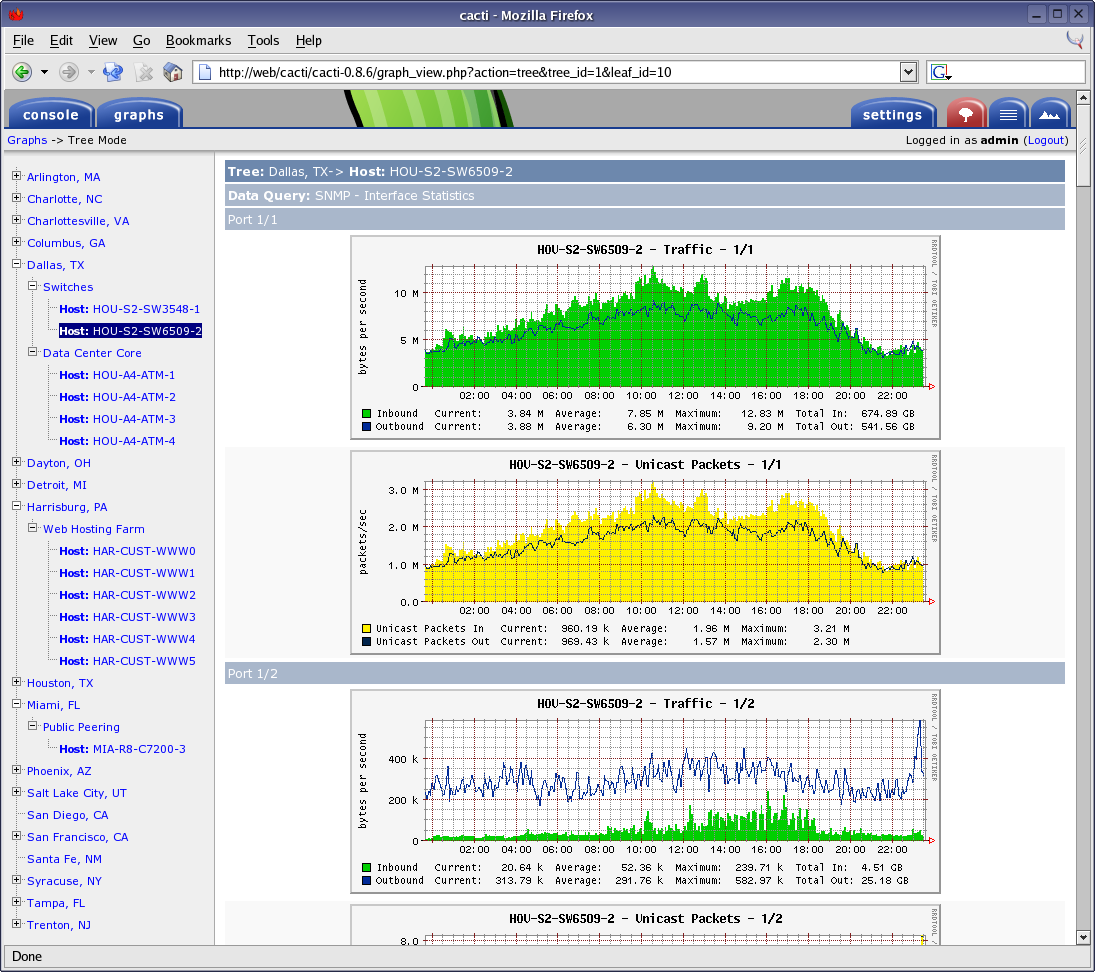
Cacti
Cacti® is another of the monitoring warhorses that has endured as a go-to for network monitoring needs. It allows you to collect data from almost any network element, including routing and switching systems as well as firewalls, and put that data into robust graphs. If you have a device, it’s possible that Cacti’s active community of developers has created a monitoring template for it.
Cacti supports SNMP polling, which itself covers a wide range of network devices. You can also extend Cacti’s capabilities to use scripts, queries, or commands for data collection, and save it as a template to use for polling other devices for similar datasets. Cacti leverages the power of RRDTool, an open-source data logging and graphing system for creating graphs from the stored datasets. RRDTool’s data consolidation lets you store collected data forever and is limited only by the size of your storage. Cacti also allows you to add multiple users and give them access with or without edit permissions, which is perfect for service providers and enterprises with a large NOC team.
Zabbix
Admittedly complex to set up, Zabbix® comes with a simple and clean GUI that makes it easy to manage, once you get the hang of it. Zabbix supports agentless monitoring using technologies such as SNMP, ICMP, Telnet, SSH, etc., and agent-based monitoring for all Linux® distros, Windows® OS, and Solaris®. It supports a number of databases, including MySQL®, PostgreSQL™, SQLite, Oracle®, and IBM® DB2®. Zabbix’s VMware® monitoring capabilities allow you to customize using any scripting or programming language, which is widely regarded as its best feature.
Zabbix is probably the most widely used open-source network monitoring tool after Nagios.
ntop
ntop, which is now ntopng (ng for next generation), is a traffic probe that uses libpcap (for packet capture) to report on network traffic. You can install ntopng on a server with multiple interfaces and use port mirroring or a network tap to feed ntopng with the data packets from the network for analysis. ntopng can analyze traffic even at 10G speeds; report on IP addresses, volume, and bytes for each transaction; sort traffic based on IP, port, and protocol; generate reports for usage; view top talkers; and report on AS information. This level of traffic analysis helps you make informed decisions about capacity planning and QoS design and helps you find bandwidth-hogging users and applications in the network. ntopng has a commercial version called ntopng pro that comes with some additional features, but the open-source version is good enough to quickly gain insight into traffic behavior. ntop can also integrate with external monitoring applications such as Nagios for alerting and provide data for monitoring.
ntopng has some limitations, but the level of network traffic visibility it provides makes it well worth the effort.
Icinga
Built on top of MySQL and PostgreSQL, Icinga is Nagios backwards-compatible, meaning if you have an investment in Nagios scripts, you can port them over with relative ease.
Icinga was created in 2009 by the same group of devs that made Nagios, so they knew their stuff. Since then, the developers have made great strides in terms of expanding both functionality and usability since then. As the Nagios pedigree might imply, its primary focus is monitoring infrastructure and services.
Spiceworks
Spiceworks offers many free IT management tools, including inventory management, help desk workflow, and even cloud monitoring, in addition to the network monitoring solution I’m focusing on here. Built on agentless techniques like WMI (for Windows machines) and SNMP (for network and *nix systems), this free tool can provide insights into many network performance issues. You can also set up customizable notifications and restart services from within the app.
Note that Spiceworks is free because most of its revenue comes from the sale of ad displays in its network. It’s a small price to pay for a free solution, but it’s something to think about before you install.
Observium Community
Observium follows the “freemium” model that is now espoused by most of the open-source community—a core set of features for free, with additional options if you pay for them. While the “Community” (i.e., free) version supports an unlimited number of devices, Observium is still careful to say that it’s meant for home lab use. This is bolstered by the fact that the free version cannot scale past a single server. Run this on your corporate network at your own risk!
The free version also enjoys a 6-month patch and update cycle. If you want fixes any faster than twice a year, you’ll have to pay for them. One of the most painful features held back from the free version is the lack of alerting capabilities. Those caveats aside, you get a full auto-discovery of your devices and metrics (using SNMP and standard protocols, as usual).
Related Top Tools for Network Monitoring
There are a few tools that aren’t monitoring solutions per-se but are so incredibly useful to the monitoring professional that we didn’t feel right leaving them out.
Wireshark
Wireshark® is an open-source packet analyzer that uses libpcap (*nix) or winpcap (Windows) to capture packets and display them on its graphical front-end, while also providing good filtering, grouping, and analysis capabilities. It lets users capture traffic at wire speed or read from packet dumps and analyze details at microscopic levels. Wireshark supports almost every protocol, and has functionalities that filter based on packet type, source, destination, etc. It can analyze VoIP calls, plot IO graphs for all traffic from an interface, decrypt many protocols, export the output, and lots more.
Wireshark provides unlimited opportunities to study packets, which makes it a solid go-to for network, system, and security admins.
Nmap
Nmap uses a discovery feature to find hosts in the network that can be used to create a network map. Network admins value it for its ability to gather information from the host about the Operating System, services, or ports that are running or are open, MAC address info, reverse DNS name, and more.
Scalability is the other big reason why network admins love Nmap. It can scan a single host or an entire network with “hundreds of thousands” of machines.
When you need to quickly map the hosts in your network, Nmap is your tool.
Free Network Monitoring Tools
Most of the tools we’ve focused on in this post have been of the “freemium” variety—a limited set of features (or support) for free, with additional features, support, or offerings available for a cost.
But there is a whole other class of tools which are just free-free. They do a particular task very well, and there is no cost (with the exception of the odd pop-up ad during installation). We wanted to take a moment to dig into a few of the tools that are in “network_utilities” directories on our systems and frequently use.
Also, we want to be clear that the list below isn’t meant to be (or even appear) exhaustive. There are many, MANY useful free network monitoring tools out there, and which ones an IT pro uses is often up to personal preference or the specifics of their work environment. We’re listing out the ones we’ve found in our travels and use often.
Traceroute NG
Ping is great. Traceroute is better. But both fall short in modern networks (and especially with internet-based targets because the internet is intrinsically multi-path). A packet has multiple ways to get to a target at any moment. You don’t need to know how a SINGLE packet got to the destination; you need to know how ALL the packets are moving through the network across time. Traceroute NG does that and avoids the single biggest roadblock to ping and traceroute accuracy—ICMP suppression—at the same time.
Bandwidth Monitor
If you are doing simple monitoring, the first question you’re going to want to know is, “is it up?” Following closely on the heels of that is, “how much bandwidth is it using?” Yes, it’s a simplistic question and an answer that may not really point to a problem (because let’s be honest, a circuit that’s 98% utilized most of the time is called “correctly provisioned” in our book), but that doesn’t mean you don’t want to know. This tool gets that information quickly, simply, and displays the results clearly.
Response Time Viewer for Wireshark
We mentioned Wireshark over in the non-monitoring monitoring tools section because of its flexibility, utility, and ubiquity. But the “-ity” that was left out was “simplicity.” That sucker can be HARD to learn to use, especially for new network engineers fresh on the job. This utility will take Wireshark data and parse it out to show some important statistics simply and clearly. Specifically, it collects, compares, and displays the time for a three-way-handshake versus the time-to-first-byte between two systems. Effectively, it shows you whether a perceived slowdown is due to the network (three-way handshake) or application response (time to first byte). This can be an effective way to narrow down your troubleshooting work and focus on solving the right problem faster.
IP SLA Monitor
IP SLA is one of the most often-overlooked techniques in a monitoring specialist’s arsenal. Relegated to being “that protocol for VoIP,” the reality is that IP SLA operations can tell you much more than jitter, packet loss, and MOS. You can test a remote DHCP server to see if it has addresses to hand out, check the response of DNS from anywhere within your company, verify that essential services like FTP and HTTP are running, and more.
So, this free tool is something of a secret weapon for engineers who need to get miraculous tasks done on the cheap.
What have we learned?
Here in 2020, monitoring professionals have almost an embarrassment of riches when it comes to free and open-source solutions to help us do our jobs. While none of these free tools are exactly push-button simple to install, maintain, or use, if your budget for tools is close to non-existing and you have the time to invest, they may fit the bill. Otherwise, we’d recommend using a tool like SolarWinds NPM, which is easy to install and supports motioning and reporting right out of the box.
The realm of Network Monitoring Tools, Software and Vendors is Huge, to say the least. New software, tools and utilities are being launched almost every year to compete in an ever changing marketplace of IT monitoring and server monitoring.
We've now in the new decade and as we're looking into 2020, you absolutely need a solution that fits all your criteria!
We've gone through as many tools as we could find and rounded up the best ones in easy to read format and highlighted their main strengths and why we think they are in the top class of tools to use in your IT infrastructure and business.
Some of the features we are looking for are Uptime/Downtime indicators, along with a robust and thorough alerting systems (via Email/SMS), custom templates and thresholds, Netflow and SNMP Integration, Automatic Network Topology Discovery and Mapping functionality, and much more.
The features from above were all major points of interest when evaluating software suites for this article and we'll try to keep this article as updated as possible with new feature sets and improvements as they are released, as newer versions of the tools below will likely be released throughout the years.
Here's a List of Top Network Monitoring Tools and Software of 2020:
Below you'll find an Updated list of the Latest Tools & Software to ensure your network is continuously tracked and monitored at all times of the day to ensure the highest up-times possible. Most of them have free Downloads or Trials to get you started for 15 to 30 days to ensure it meets your requirements.
1. Solarwinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is easy to setup and can be ready in no time. The tool automatically discovers network devices and deploys within an hour. Its simple approach to oversee an entire network makes it one of the easiest to use and most intuitive user interfaces.
The product is highly customizable and the interface is easy to manage and change very quickly. You can customize the web-based performance dashboards, charts, and views. You can design a tailored topology for your entire network infrastructure. You can also create customized dependency-aware intelligent alerts and much more.
The software is sold by separate modules based on what you use. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor Price starts from $1,995 and is a one-time license including 1st-year maintenance.
Solarwinds NPM has an Extensive Feature list that make it One of the Best Choices for Network Monitoring, including:
- Automatically Network Discovery and Scanning for Wired and Wifi Computers and Devices
- Support for Wide Array of OEM Vendors
- Forecast and Capacity Planning
- Quickly Pinpoint Issues with Network Performance with NetPath™ Critical Path visualization feature
- Easy to Use Performance Dashboard to Analyze Critical Data points and paths across your network
- Robust Alerting System with options for Simple/Complex Triggers
- Monitor CISCO ASA networks with their New Network Insight™ for CISCO ASA.
- Monitor ACL‘s, VPN, Interface and Monitor on your Cisco ASA
- Monitor Firewall rules through Firewall Rules Browser
- Hop by Hop Analysis of Critical Network Paths and Components
- Automatically Discover Networks and Map them along with Topology Views
- Manage, Monitor and Analyze Wifi Networks within the Dashboard
- Create HeatMaps of Wifi Networks to pin-point Wifi Dead Spots
- Monitor Hardware Health of all Servers, Firewalls, Routers, Switches, Desktops, laptops and more.
- Real-Time Network and Netflow Monitoring for Critical Network Components and Devices

More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
2. PRTG Network Monitor from Paessler
Mac Monitoring Software Free
PRTG Network Monitor software is commonly known for its advanced infrastructure management capabilities. All devices, systems, traffic, and applications in your network can be easily displayed in a hierarchical view that summarizes performance and alerts. PRTG monitors IT infrastructure using technology such as SNMP, WMI, SSH, Flows/Packet Sniffing, HTTP requests, REST APIs, Pings, SQL and a lot more.
It is one of the best choices for organizations with low experience in network monitoring. The user interface is really powerful and very easy to use.
A very particular feature of PRTG is its ability to monitor devices in the datacenter with a mobile app. A QR code that corresponds to the sensor is printed out and attached to the physical hardware. The mobile app is used to scan the code and a summary of the device is displayed on the mobile screen.
PRTG has a very flexible pricing plan, to get an idea visit their official pricing webpage below.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
3. ManageEngine OpManager
At its core, ManageEngine OpManager is an infrastructure management, network monitoring and Application Performance Management “APM” (with APM plug-in) software.
The product is well balanced when it comes to monitoring and analysis features.
The solution can manage your network, servers, network configuration and fault & performance; It can also analyze your network traffic. To run Manage Engine OpManager, it must be installed on-premises.
A highlight of this product is that it comes with pre-configured network monitor device templates. These contain pre-defined monitoring parameters and intervals for specific device types.
The essential edition product can be purchased for $595 which allows up to 25 devices.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
4. WhatsUp Gold 2017
WhatsUp Gold (WUG) is a network monitoring software from Ipswitch. It is one of the easiest to use and highly configurable tools in the market. The dashboards are user-friendly and visually attractive.
For daily IT management, WhatsUp Gold is a price/feature balanced network monitoring tool. It is also completely customizable. Dashboards can be customized to display your IT infrastructure and alerts to fit your requirements.
The highlights of the newest 2017 Plus version are hybrid cloud monitoring, real-time performance monitoring, automatic and manual failover and extended visibility to distributed networks.
WhatsUp Gold is limited for Windows OS support. This software comes with different pricing plans to adjust to your network and wallet. Compare different editions in their official website and ask for a price quote.

More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
5. Nagios XI
Nagios XI is aimed at a wide audience, from freelancers, SMBs (Small-to-Medium-Business), to large corporations. This makes Nagios’s XI pricing model one of the most flexible. They have a free version, open-source, one-time license and subscription. It is one of the few tools that allows an extreme flexibility (because of its adaptability to plug-ins) on what’s being monitored and alerted for a low cost.
Nagios XI focuses on monitoring. The key IT components that Nagios XI monitors are Network, Infrastructure, and Database. Although the software is easy to install, it will initially take some time to adjust to your requirements. This is because Nagios XI does not auto-discover devices. You have to configure each device that needs to be monitored with a configuration file.
Standard paid edition starts from $1,995 for 100 nodes. Nagios XI is supported only by Linux (or UNIX variants) OS.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
6. Zabbix
Zabbix is an open source monitoring tool. It is popular for its easy-to-use and pleasing Web GUI that is fully configurable. Zabbix focuses on monitoring and trending functionality. This software is frequently used for monitoring servers and network hardware. One of the highlights of Zabbix is that it can predict trends in your traffic. Zabbix can forecast future behavior based on historical data.
Since it is open source, it has an active user community spread around the world and good documentation. Zabbix gives the freedom to use the open-source solution without vendor lock-ins (including all components).
Zabbix is powerful for SMB networks below 1,000 nodes. Over that, the software can get slower and its performance decreased. Another disadvantage is that it doesn’t include real-time tests and reports.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
7. Incinga
It is another open source infrastructure and service monitoring tool. Icinga was developed in 2009 by the same team of developers that brought you Nagios.
It is a very easy to use and flexible tool for SMB and enterprise networks. The software focuses strongly on monitoring infrastructure and services. The tool also includes great threshold analysis and report/alert functionalities.
Icinga is popular at providing superior alters and reports of the general health of your IT infrastructure. All alert dependencies can be displayed in the dashboard and sent via email, SMS or mobile message applications.
Since Icinga is open source it is completely free. With its strong community forum, you can get all support you need.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
8. Datadog
It is a monitoring service specially designed for hybrid cloud environments. Datadog can also monitor the performance of network, apps, tools, and services.
One of the highlights of Datadog is that it can provide extensibility though many APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) with very good documentation.
The software is very easy to install and can be up and running in on time. To make it easy, agents can download and install the software. The agents are available for various different platforms such as Windows, Mac OS, Several Linux distributions, Docker, Chef, Puppet, etc.
You can create custom graphs, metrics, and alerts in an instant, and the software can adjust them dynamically based on different conditions. Datadog prices start from free (up to five hosts), Pro $15/per host, per month and Enterprise $23 /per host, per month.
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
9. ConnectWise Automate
Formerly known as Labtech, ConnectWise Automate is a new cloud-based manager and monitoring solution that can keep track of your IT infrastructure devices from a single location.
ConnectWise Automate discovers all devices in your network so they can be monitored proactively. The network visibility is improved because the tool interprets problems and initiates an automatic pre-defined action to mitigate the issue.
A cool feature of this software is the “Patch Management”, as it allows you to protect all your systems with simultaneous patching from a centralized manager. Use Windows Patch management or third-party software.
By extending the ConnectWise suite, the software can also allow a premier remote control. You can resolve issues quickly by allowing remote support, remote access and even remote meetings.
ConnectWise Automate is aimed at SMBs. The price of the software is based on quotes. You can get a price on their official site tailored accordingly to the size of your network.
Free Internet Monitoring Software Mac
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
10. Logic Monitor
LogicMonitor is an automated SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) IT performance monitoring tool. With LogicMonitor you can get full visibility of the performance and health of your network.
This software will automatically discover IT infrastructure devices and monitor them proactively. Besides from extraordinary monitoring capabilites, the software also improves the performance and health of your network. LogicMonitor can help identify incoming issues by providing predictive alters and trend analysis.
Logic Monitor is popular because it comes with a highly customizable dashboard, alerts, and reports. The software supports over 1000 different technologies, including hybrid cloud and networking devices, in order to provide granular performance metrics.
To get a price you can request a quote from LogicMonitor’s official pricing site.
Free Network Monitoring Tools For Mac
More Information and Official Website:
Download Link:
Free Network Monitoring Tools For Mac
11. OP5 Monitor
OP5 Monitor is OP5’s Enterprise level monitoring solution. With OP5 Monitor you can monitor applications, networks, servers and storage, regardless of location, whether that’s on-premise, hybrid or in a private/public cloud.
OP5 Monitor is also Nagios compatible, meaning that it’s easy to migrate from Nagios and re-use existing agents and plugins.
Key features include:
- Unified Dashboard – Fully customizable and interactive dashboards
- Scalability- Unparalleled Scalability across Distributed Environments
- Automation – Endless Possibilities To Automate
- API- Developer Friendly Interface
- SNMP Traps – Read, process and generate alerts from SNMP traps
- Reporting – Custom, SLA- reports and availability reports.
OP5 Monitor is free for up to 20 devices, and has a pricing plan based on your specific requirements.
Network Monitoring Mac
More Information and Official Website:
Remote Monitoring Mac
Download Link: